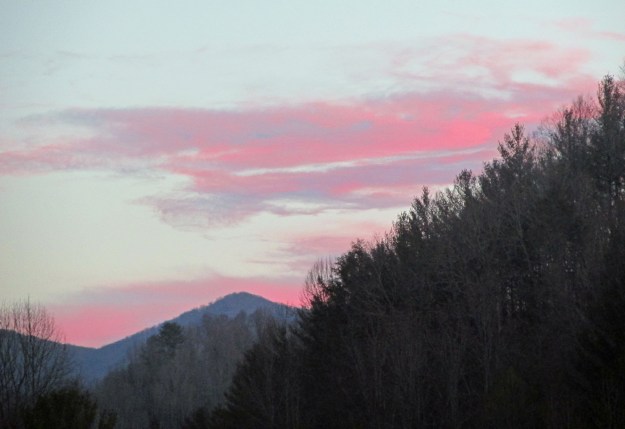
Photo by Bryan Stevens • The setting sun casts a pink glow to the winter sky near the village of Roan Mountain. The 11th annual Roan Mountain Winter Naturalists Rally is set for Saturday, Feb. 11, at the Roan Mountain State Park Conference Center.
Activities last month and planned events for February are just some of the evidence that, no matter the season, things are always happening on Roan Mountain.
For instance, the 65th Roan Mountain Christmas Bird Count was held Sunday, Dec. 17, with nine observers in two parties. Up to four inches of snow blanketed most of the area, but the roads were clear. These weather conditions highlight the fact that over the years a couple of Roan Mountain CBCs had to be cancelled due to weather conditions.
Participants included Fred Alsop, Jim Anderson, Rick Blanton, Kevin Brooks, compiler Rick Knight, Roy Knispel, Guy McGrane, Amber Stanley, and Charles Warden. A total of 44 species were tallied, near the 30 year average of 46. The all-time high of 55 species was established back in 1987.

Photo by Bryan Stevens • A total of 50 Dark-eyed Juncos made the tally during the Roan Mountain Christmas Bird Count held Dec. 17, 2017.
A list of the species follows:
Canada Goose, 24; Pied-billed Grebe, 1; Great Blue Heron, 3; Cooper’s Hawk, 1; Red-shouldered Hawk, 1; and Red-tailed Hawk, 6.
Rock Pigeon, 19; Mourning Dove, 58; Eastern Screech-Owl, 2; Barred Owl, 1; Red-bellied Woodpecker, 3; Yellow-bellied Sapsucker, 2; Downy Woodpecker, 10; Hairy Woodpecker, 2; Northern Flicker, 1; and Pileated Woodpecker, 7.
American Kestrel, 1; Eastern Phoebe, 6; Blue Jay, 23; American Crow, 82; and Common Raven, 11.
Carolina Chickadee, 25; Tufted Titmouse, 20; Red-breasted Nuthatch, 5; White-breasted Nuthatch, 15; Brown Creeper, 2; Winter Wren, 2; Carolina Wren, 15; Golden-crowned Kinglet, 13; Eastern Bluebird, 30; American Robin, 12; Northern Mockingbird, 6; European Starling, 65; and Cedar Waxwing, 2.

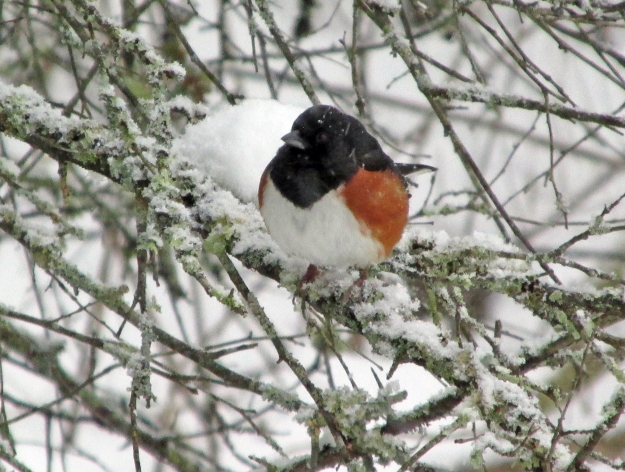
Photo by Bryan Stevens • A total of 15 Northern Cardinals were found the day of the Roan Mountain Christmas Bird Count last month.
Eastern Towhee, 9; Field Sparrow, 11; Song Sparrow, 80; Swamp Sparrow, 2; White-throated Sparrow, 11; Dark-eyed Junco, 50; Northern Cardinal, 15; House Finch, 3; American Goldfinch, 46; and House Sparrow, 41.
Some interesting incidents on this count included finding an Eastern Phoebe at an elevation of 4,450 feet surrounded by snow. The most abundant birds included Common Crow with 83 individuals found and European Starling with 65 individuals counted.
•••••••
The focus will be on botany for the upcoming Roan Mountain Winter Naturalists Rally, scheduled for Saturday, Feb. 11.

Lisa Huff
According to Richard Broadwell, director for the winter rally, the event has drawn hardy nature enthusiasts from far and wide to Roan Mountain for the past 11 winter seasons. Top naturalists volunteer their time and energy to make the event both enjoyable and educational for people of all ages. Parents are encouraged to bring the kids.
Broadwell noted that the 2018 Winter Rally continues this celebration of the natural world by providing top speakers on topics concerning the environs of the Roan Highlands. Speakers for morning programs will be Ben Jarrett, Southern Regional Science Coordinator, for The American Chestnut Foundation; Lisa Huff, Stewardship Ecologist with the Tennessee State Natural Areas Program; and Dwayne Estes, professor of biology at Austin Peay State University.
Jarrett will speak about the historical significance of the American chestnut in a program tilted “Restoration of American Chestnut: A Marriage of Breeding and Biotechnology.” He will take a look at the American chestnut and its economic, ecological and social importance). He will also educate about the chestnut blight and subsequent downfall of the species, as well as the ongoing restoration efforts through backcross breeding and genetic engineering.

Ben Jarrett
Huff will present a history of the shortleaf pine and bluestem vegetation community in Tennessee in a program titled “The Mystery of the Missing Shortleaf Pine.” She started working for the Tennessee State Natural Areas Program in 2000. She is tasked with the daily operations and management of over 42,000 acres in 21 natural areas in East Tennessee.
Estes will speak about southeastern United States grasslands, such as savannas, prairies, glades, barrens, bald, bogs, fens, and meadows, all of which are imminently threatened. He will also educate about the work of the Southeastern Grasslands Initiative in Clarksville, which aims to focus grassland conservation efforts across a 21-state region. SGI will use a multi-faceted approach combining restoration, preservation, recreation, research, rescue, seed banking, education and market-driven strategies. SGI is currently working with and seeking support from private philanthropic foundations, corporations, non-profit conservation organizations and government agencies. His program is titled “The Southeastern Grasslands Initiative: Charting a New Course for Conservation in the 21st Century.”

Dwayne Estes
All programs will be held at the Roan Mountain State Park Conference Center. Jarrett will speak at 9:30 a.m. followed by Huff at 10:30 a.m. The program by Estes at 11:40 a.m. will conclude the slate of presentations. Lunch, which requires a pre-paid reservation, will be served at 12:30 p.m. Sarah Sanford, candidate for Master’s of Environmental Management at Duke University, will present a lunchtime program on “Grassy Balds Management in the Roan Highlands.”
Four different hikes are planned for the afternoon, starting at 1:30 p.m. Hike options include:
• Lisa Huff will lead a hike in the Hampton Creek Cove Natural Area. Binoculars are recommended. The moderately strenuous hike should not take more than three hours.
• Jamey Donaldson, ETSU John C. Warden Herbarium Adjunct Curator, will lead a hike to the alder balds on the ridgeline of Roan Mountain. Dress warmly for this strenuous hike.

Photo by Bryan Stevens • A Pine Siskin in a spruce at Carver’s Gap on Roan Mountain.
• Marty Silver, Ranger with Warriors Path State Park, will lead a wildlife tracking and animal signs hike down near the Doe River in Roan Mountain State Park. This is a moderately strenuous and kid-friendly activity.
• Dr. Frosty Levy, Professor Emeritus of Biology at East Tennessee State University, will lead an easy winter tree identification hike in Roan Mountain State Park.
For more information and a downloadable brochure, visit http://friendsofroanmtn.org/2018%20Winter%20Rally%20Brochure.pdf or email Broadwell at rbroadwell@gmail.com. The event is free to members of Friends of Roan Mountain and children. Adults who are not members of FORM can register for all activities for $10.