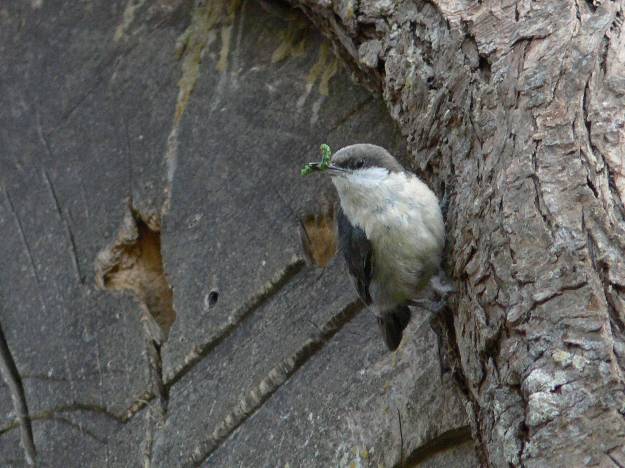
Photo by Lee Karmey/USFWS • A pygmy nuthatch captures a caterpillar.
Veronica Rausch contacted me by email to share a story of the nuthatches that frequent the feeders at her home in central Oregon.
“I have a small flock of pygmy nuthatches coming into the feeders next to my dining room window on a regular basis,” Veronica wrote, adding that the nuthatches began their visits about three weeks ago.
Veronica wrote that she lives in the pine forests of Central Oregon at an elevation of about 4,200 feet.
“The pygmy nuthatches are delightful little birds and share the feeders with the chickadees and juncos,” she wrote. “The bigger birds such as the Stellar’s jays and the woodpeckers will cause them to leave.”
Veronica has also enjoyed observing their unusual antics. “I saw one do a little dance on a branch by the suet feeder,” she described in her email. “Unfortunately, I wasn’t able to grab the camera fast enough! I hope they stick around.”
I replied to Veronica’s email, noting how I consider her fortunate to be hosting the smallest of North America’s nuthatches at her home. Admitting to some envy at her good fortune, I explained that I hope to some day add this species to my life list so I can check all of the continent’s nuthatches off my list of target birds.
Even by nuthatch standards, the pygmy nuthatch is a small bird. In appearance, this nuthatch shows buffy-white underparts contrasted with a brown head and a slate-gray back. They often breed in large extended family flocks, so the four individuals observed by Veronica might very well have been closely related to each other.
Nesting pygmy nuthatches are often assisted in their chores by “nest helpers,” which are close relatives that help the busy parents gather food and feed hungry young. These nest helpers also deliver food to females as they incubate eggs and will mount a spirited defense of a nest threatened by intruders. Their communal nature extends to nocturnal roosting when many individuals will huddle together to ensure their combined body heat helps them survive extremely cold nights.
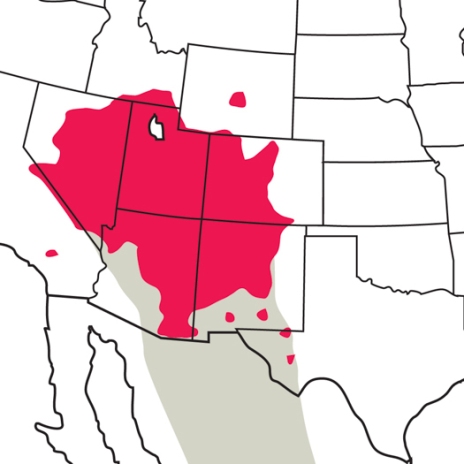
So how small is the pygmy nuthatch? The adults are barely four inches long and weigh only a third of an ounce. A common fountain pen weighs more than this tiny nuthatch, which goes a long way towards explaining the bird’s scientific name, sitta pygmaea.

Photo by theSOARnet/Pixabay.com • The brown-headed nuthatch, the southeastern counterpart to the pygmy nuthatch that ranges throughout the Rocky Mountain states, is strongly associated with various types of pine trees.
Pygmy nuthatches are not at all likely to be found in the Mountain Empire or any adjacent areas, but there is another small nuthatch that is found in some extremely localized habitats in the region. The brown-headed nuthatch is a specialist of pine woodlands throughout the southeastern United States, favoring loblolly-shortleaf pines and longleaf-slash pines. This nuthatch requires standing dead trees for nesting and roosting. They forage for food, however, on live pines. The birds are more abundant in older pine stands.
I saw several brown-headed nuthatches during a recent stay on Fripp Island in South Carolina. I’ve also observed this small nuthatch during visits to Chattanooga, Tennessee, and Atlanta, Georgia, as well as various other locations in South Carolina. This nuthatch even occurs in the Mountain Empire region, most recently with four of these birds being found at Washington County Park on South Holston Lake near Bristol during the 2018 Christmas Bird Count conducted by the Bristol Bird Club.
These small birds will occasionally forage close to the ground, but they are often in the upper branches of pine trees. Their presence is often revealed by their call, which sounds amazingly like a squeeze toy. They produce their “squeaky toy” call persistently when agitated or curious. Brown-headed nuthatches often associate with mixed flocks in company with Carolina chickadees, tufted titmice, pine warblers and other small songbirds.
The power of flight gives most birds a perfectly valid reason to disregard the power of gravity. The family of tree-clinging birds known as nuthatches lives an even more topsy-turvy lifestyle than many other of their winged kin. Nuthatches prefer a headfirst stance, even “walking” upside down as they search for food in the nooks and crannies of tree trunks and branches.
The United States is home to four species of nuthatches: white-breasted, red-breasted, brown-headed and pygmy. White-breasted nuthatches are probably the most familiar nuthatch to backyard birders in this area.
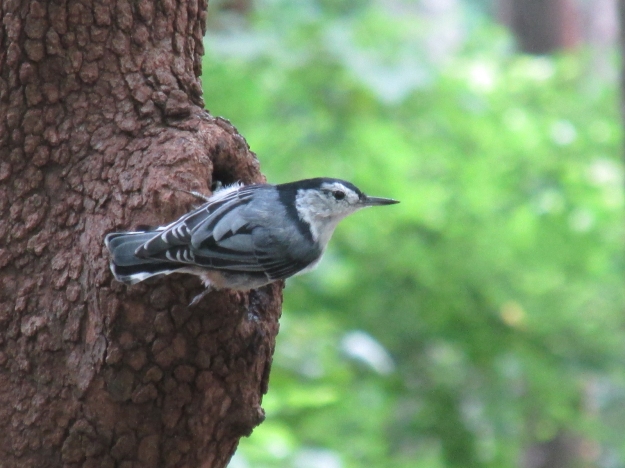

Photo by Bryan Stevens • A white-breasted nuthatch clings to the bark of a tree.
Because of their gravity-defying antics, the white-breasted nuthatch and other members of the family can provide hours of entertainment at our bird feeders. Individual white-breasted nuthatches will follow a single-minded path along the trunk of a tree or a branch on the way to a feeder. An individual nuthatch rarely varies from this path. It’s amusing to watch the jerky progress along the trunk as this bird prepares for a flight to a feeder holding sunflower seeds or a hanging wire basket of suet.
At my home, nuthatches typically remain aloof from the always-ongoing rivalry between the chickadees and titmice. The white-breasted nuthatch is also a no-nonsense visitor. Rarely distracted by disturbances among other birds, this nuthatch is content to grab a seed and go or hang on to the wire frame of a suet basket and peck off chunks of suet.
The more numerous titmice and chickadees give way when a white-breasted nuthatch claims a feeder. At times, however, among the frantic activity, a tufted titmouse or a Carolina chickadee will forget itself and fly to a position on a feeder already claimed by a nuthatch. If surprised enough to retreat to a nearby perch, the nuthatch will go through a rather comical little dance to express its displeasure. Wings spread out in a rigid pose, the bird will turn around in tight circles, showing definite resentment at being displaced by an offending chickadee or titmouse.
The stubby red-breasted nuthatch is another member of the family that occasionally finds its way to our yards. Smaller than the related white-breasted nuthatch and, as far as I can tell, complacent in the company of chickadees and titmice, the red-breasted nuthatch is always a welcome visitor. It has a tell-tale “yank yank” call that it produces when excited that sounds very much like little tin horns. The red-breasted nuthatch, perhaps because it spends so much of the year in more remote areas, can also be amazingly tame when it pays a winter visit.
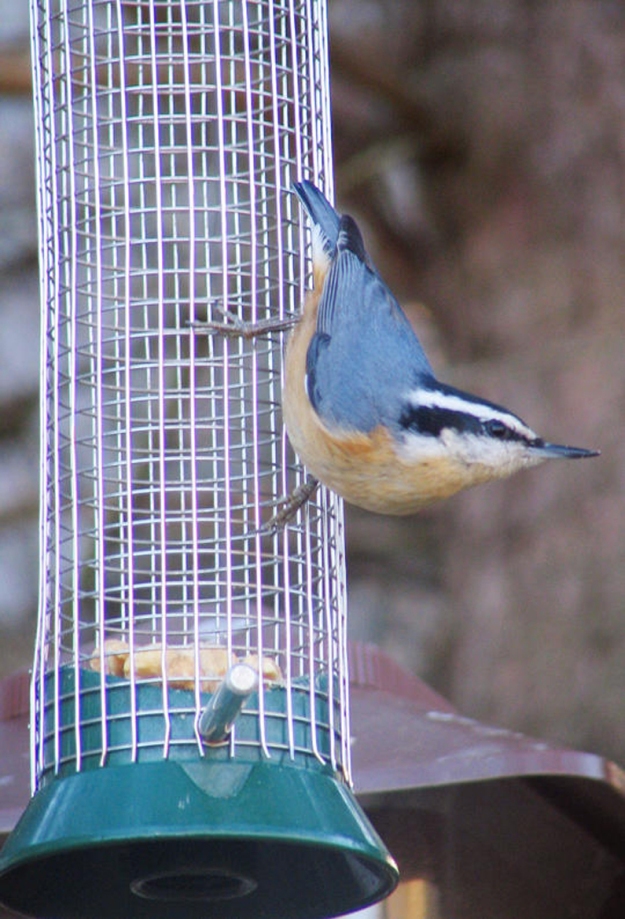

Photo by Bryan Stevens • A red-breasted nuthatch clings to the mesh of a feeding tube to get at the peanuts contained within.
Nuthatches can be attracted to feeders by offering peanuts, sunflower seeds and suet. They are also cavity-nesting birds, but are more reluctant about accepting a nesting box as a place to rear young. They will gladly accept an old woodpecker hole or other natural cavity in a tree.
I also want to complete my list of North American nuthatches by adding the fourth species — pygmy nuthatch — to my life list. I have made two trips to western North America, where this species ranges, but haven’t managed to find this bird. Both the pygmy and brown-headed are among the smallest members of the nuthatch family.
On the other end of the size scale is the appropriately named giant nuthatch, which reaches a length of almost eight inches. The giant nuthatch ranges through China, Thailand and Burma. This nuthatch is bigger than a downy woodpecker, one of our more common visitors at backyard feeders in our region.
Worldwide, there are about 25 species of nuthatches, some of which have surprisingly descriptive names for birds that spend most of their lives creeping in obscurity along the trunks and branches of trees. Some of the more creative common names for these little birds are inspired by locations around the globe, giving us species like Siberian nuthatch, Kashmir nuthatch, Burmese nuthatch, Bahama nuthatch, Algerian nuthatch, Indian nuthatch and Chinese nuthatch.
These birds are named “nuthatch” for the habit of some species to wedge a large seed in a crack and hack at it with their strong bills. I like to refer to them as “upside-down birds” because of their gravity-defying nature. It must give them an interesting perspective on the world around them.
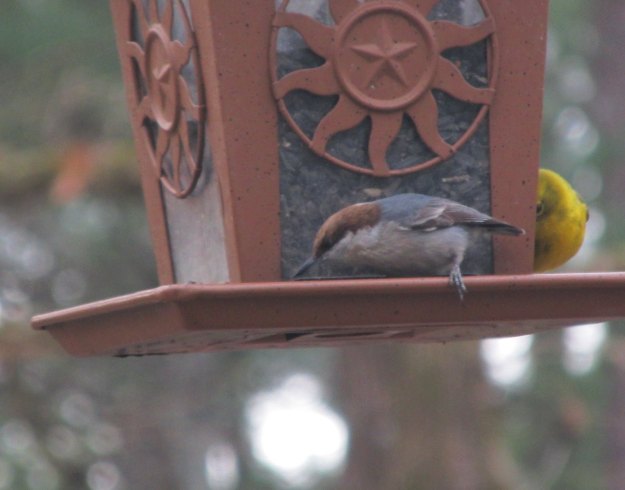

Photo by Bryan Stevens • In some areas, brown-headed nuthatches are feeder visitors. These small nuthatches are specialists that favor stands of loblolly pine.